OKI Develops Mass-Production Technology For Multi-Layer Copper-Coin Printed Circuit Boards To Support High Speeds And High Frequencies
Proprietary OKI T-Coin structure achieves 20-fold improvement in heat dissipation for large-volume data communications
OKI Circuit Technology, an OKI group company responsible for printed circuit board business, has successfully developed design and mass production technologies for multi-layer printed circuit boards that support high speeds and high frequencies(*1) based on copper coin(*2) insertion. The new technology achieves a 20-fold improvement in heat dissipation over existing technologies. Mass production of printed circuit boards based on the new technology began in April 2015 for use in the latest large-volume data communication devices. Sales forecasts for this fiscal year are 200 million yen.
With data communications volumes expanding alongside the ever-improving performance of mobile devices like smartphones, the issue of countermeasures against heat generated by high-speed, high-frequency components that process large volumes of data on base stations and servers at data centers has emerged as a crucial issue. There are also growing demands for high-density mounting of semiconductors and other electronic components on small printed circuit boards to reduce equipment size, as well as demands for the elimination of cooling fans and heat sinks from equipment to reduce size and power consumption. Increasingly, printed circuit boards need advanced heat-dissipating structures to more efficiently conduct heat generated by electronic components mounted in confined areas to the printed circuit board and dissipate it to the external environment.
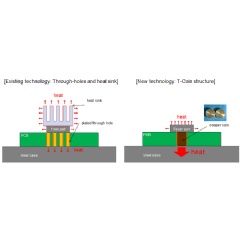
Materials designed for use at high speeds and high frequencies tend to have lower structural strength than conventional printed circuit boards. Inserting copper coins, which subjects through-holes to loads, was previously considered difficult for multi-layer boards. The conventional mainstream method for ensuring heat dissipation has been “through-hole construction,” whereby many through-holes are drilled in the printed circuit board and their surfaces are copper-plated to dissipate heat. However, with electronic components packed at ever-greater densities to handle ever-higher data volumes, the amount of heat to be dissipated has increased, while the space available for providing through-holes to dissipate heat has shrunk. This trend has made measures for achieving adequate heat dissipation an increasingly urgent issue.
In response, OKI Circuit Technology successfully developed a new “T-Coin (Technology of copper Coin insert) structure” (Figure 1) that increases the area available for heat conduction for a limited number of through-holes by inserting cylindrical copper (copper coins) into through-holes without leaving gaps using a specially-developed method that minimizes pressure loading. “This technology improves heat dissipation performance 20-fold while ensuring high reliability and long service life. Heat-generating components are in direct contact with large areas of copper with high thermal conductivity(*3), ensuring high heat dissipation performance,” says Masahito Nozue, President of OKI Circuit Technology. “The technology is expected to contribute to the development of products that achieve adequate heat dissipation performance, even without cooling fans or heat sinks.”
The newly developed T-Coin structure was made possible by manufacturing techniques that control the shape and thickness of the copper coins to micron levels, along with machining pressure rate control techniques that prevent damage when copper coins make contact with the through-hole plating. The technology is compatible with a wide range of copper coin diameters (3.0 mm to 6.0 mm) and printed circuit board thicknesses (1.0 mm to 2.0 mm) for ready customization and application to all stages of the process, from simulation and prototyping to mass production of printed circuit boards, for a wide range of uses. In the lead-up to the start of mass production, OKI Circuit Technology developed and introduced a copper coin insertion apparatus based on its own specifications to ensure uniform pressure when inserting copper coins into through-holes.
Glossary
*1 : High speeds and radio-frequencies
Expanding Internet use has generated demand for the high-speed transmission of large volumes of data, such as transmitting several hundred megabytes to several gigabytes of data on the per-second timescale. Similarly, rising operating frequencies of digital circuits, now at around several gigahertz, also needs to be taken into consideration. Printed circuit boards that support high speeds and high frequencies use materials characterized by high relative permittivity and high dielectric dissipation factor.
*2 : Cooper coin
Copper material molded into cylinders.
*3 : Thermal conductivity
Refers to the ease with which heat is transmitted by conduction inside a substance from hot regions to colder regions; typically expressed in units of W/m.K (watts per meter Kelvin).
About OKI Electric Industry (OKI)
Founded in 1881, OKI Electric Industry is Japan’s leading telecommunications manufacturer in the Info-telecom field. Headquartered in Tokyo, Japan, OKI provides top-quality products, technologies, and solutions to customers through its info-telecom systems and printer operations. Its various business divisions function synergistically to bring to market exciting new products and technologies that meet a wide range of customer needs in various sectors. Visit OKI’s global website at http://www.oki.com/.
( Press Release Image: https://photos.webwire.com/prmedia/2/197738/197738-1.jpg )
WebWireID197738
This news content was configured by WebWire editorial staff. Linking is permitted.
News Release Distribution and Press Release Distribution Services Provided by WebWire.